Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a chemical process used to create layers with different applications on different surfaces. In this deposition method, the desired surface (substrate) is exposed to the vapor of one or more chemicals. Then, in order to create a solid layer with the desired chemical composition, the gas atoms in the chamber decompose on the surface of the substrate or react with each other chemically. This deposition method is classified in different ways depending on what chemical method it starts with.
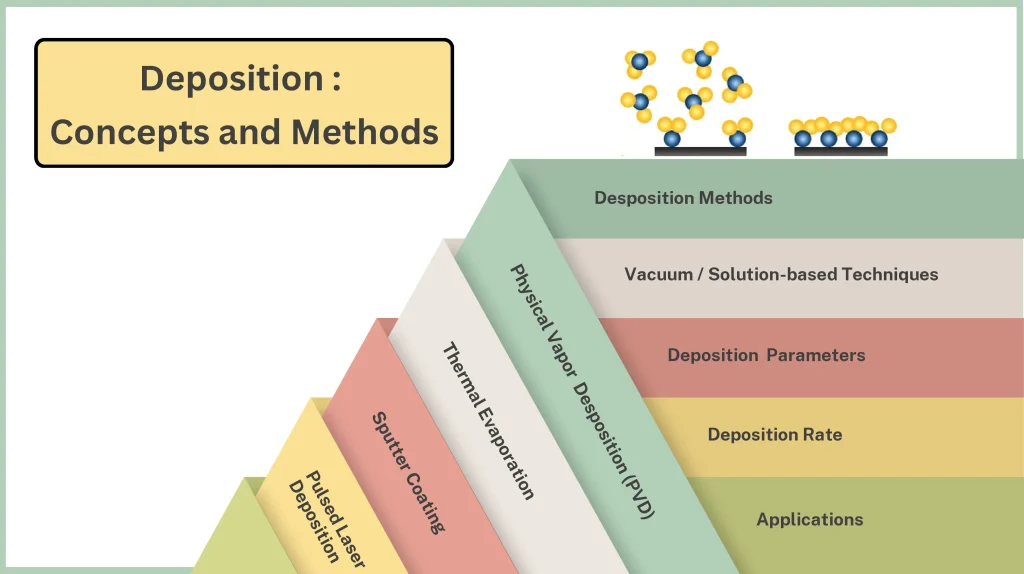
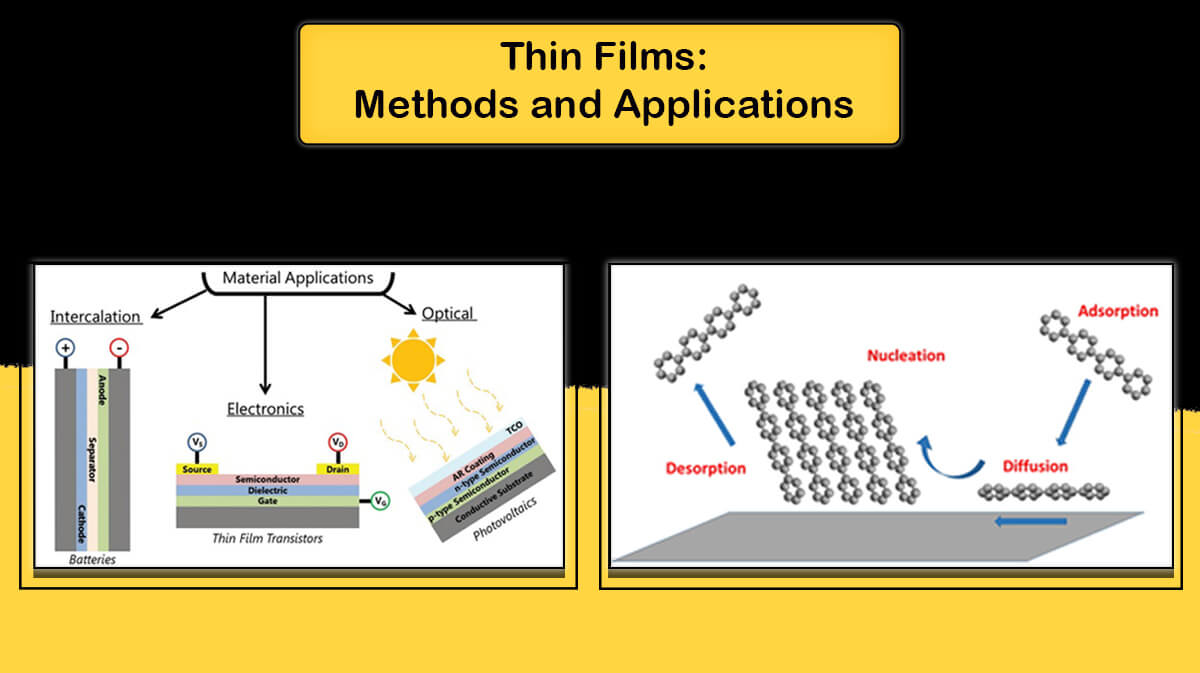
Deposition is a set of processes used to create thin or thick layers of a substance atom-by-atom or molecule by molecule on a solid surface. The created layer deposits as a coating on a surface and changes the properties of the substrate surface depending on the application.
Classification Based on Process Pressure
- Atmospheric Pressure CDV Process (APCVD)
- Low Pressure CVD Process (LPCVD)
- Ultra-High Vacuum CVD Process (UHVCVD)
Classification Based on Physical Properties of Steam
- Deposition by CVD method in which the desired atoms for the coating are transferred to the substrate by liquid/gas aerosol (Aerosol Assisted CVD(AACVD))
- Deposition by CVD method in which the material is liquid and injected directly into the evaporation chamber (Direct Liquid Injection CVD (DLICVD))
Classification Based on Substrate Heating
- The CVD process in which the chamber is heated by an external power supply and the substrate is heated by irradiation of the heated chamber walls (Hot Wall CVD)
- CVD process in which the substrate is heated directly by induction or passing current. The walls of the chamber are at room temperature (Cold Wall CVD)
Plasma Methods
- Microwave Plasma-Assisted CVD (MPCVD)
- CVD process that uses plasma to promote chemical reactions (Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD))
- Atomic-Layer CVD (ALCVD)
- Combustion Chemical Vapor Deposition (CCVD)
- Chemical and Physical Vapor Deposition hybrids
- Initiation of the process by optical decomposition of the material
Using the chemical vapor deposition method, a variety of nanostructures can be created, such as ceramic nanostructures, carbides, and carbon nanotubes. Due to the high speed of this method, it is possible to use it to produce various nanostructures industrially. However, the disadvantages of this method are that it is difficult to create and control the temperature in this method, due to the fact that it uses very high temperatures.
CVD vs. PVD
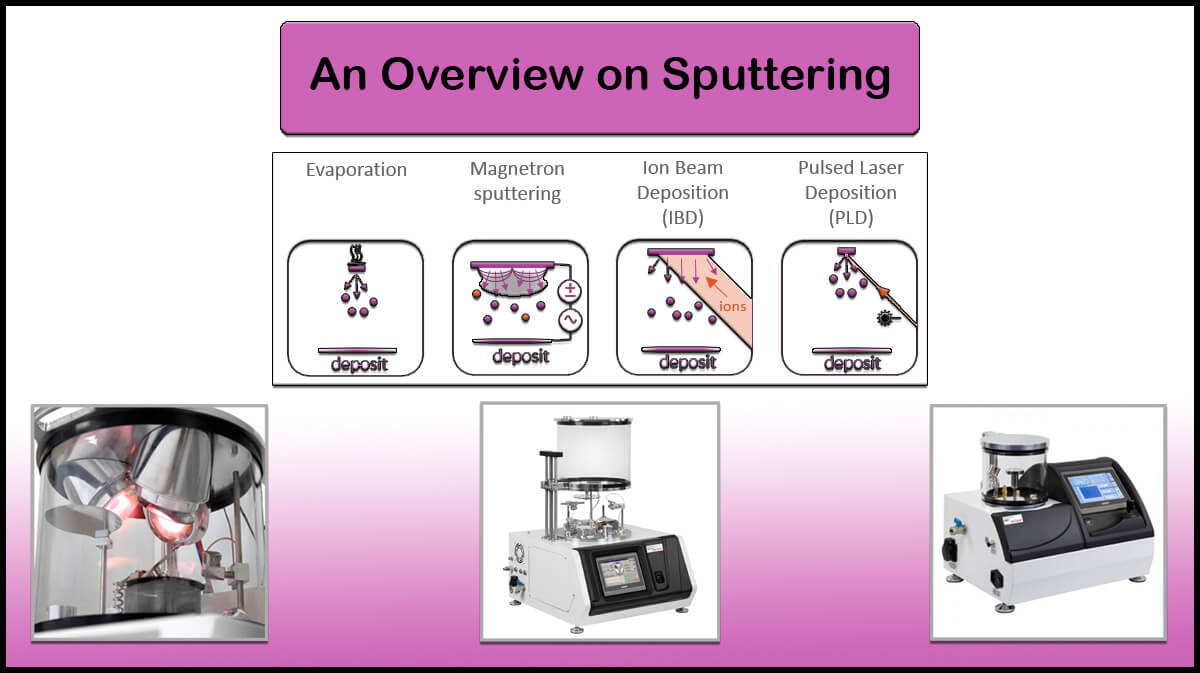
The created temperature gradient makes it difficult to control the shape and structure of the particles and the thin film created by this method and reduces the final quality of the deposited layer. In addition, the energy consumption of the CVD method is very high. One of the advantages of CVD method over physical vapor deposition (PVD) method is its cheapness.
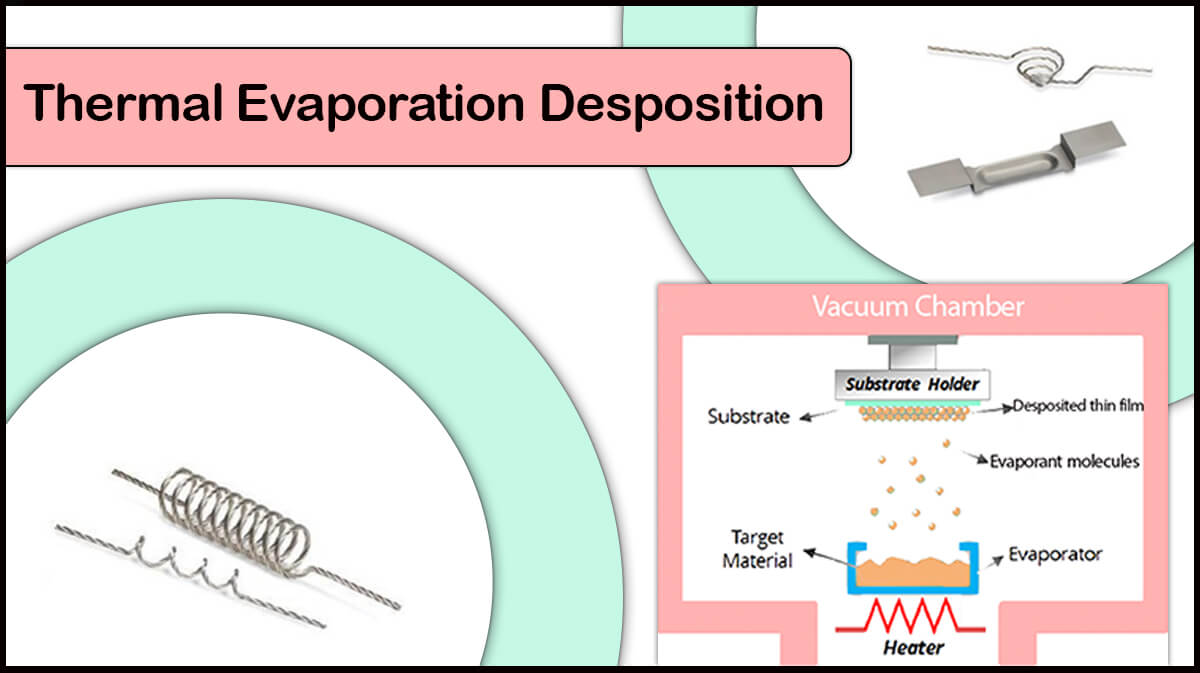
The products of Vac Coat Ltd. are in the category of PVD method deposition systems. Various PVD methods such as sputtering, thermal evaporation, pulsed laser deposition are some of the mechanisms that Vac Coat’s machines use to create nanometer to micrometer layers.