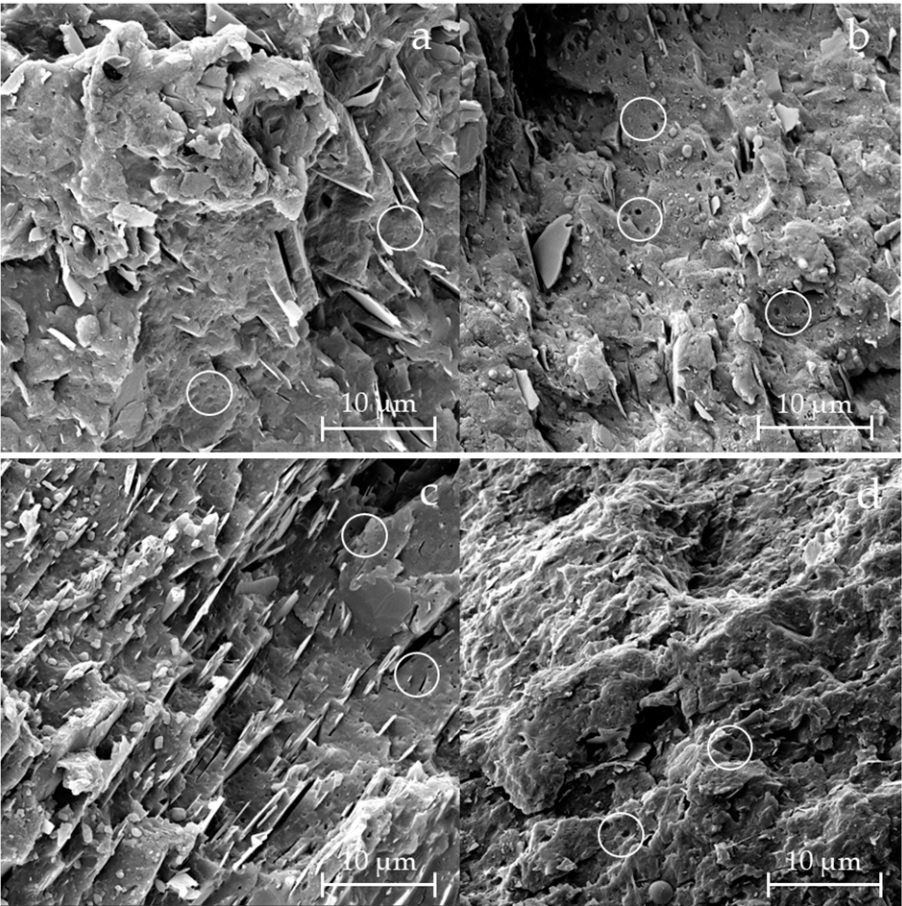
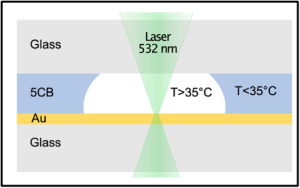
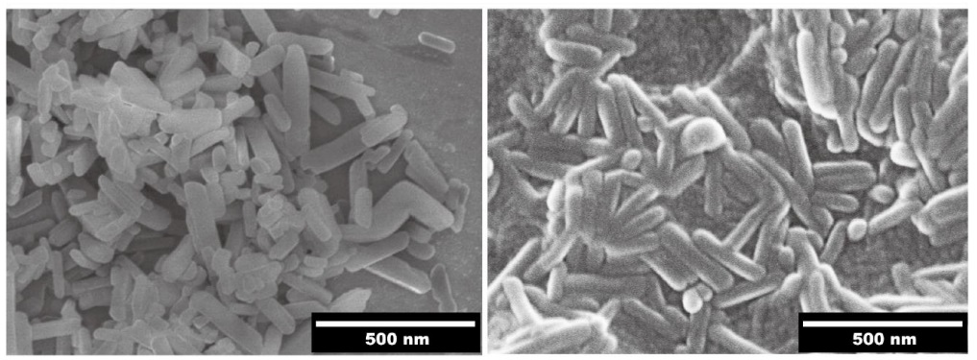
Sputter Coating by DSCT for Improved FE-SEM Imaging of Metal Organic Frameworks (MOFs)
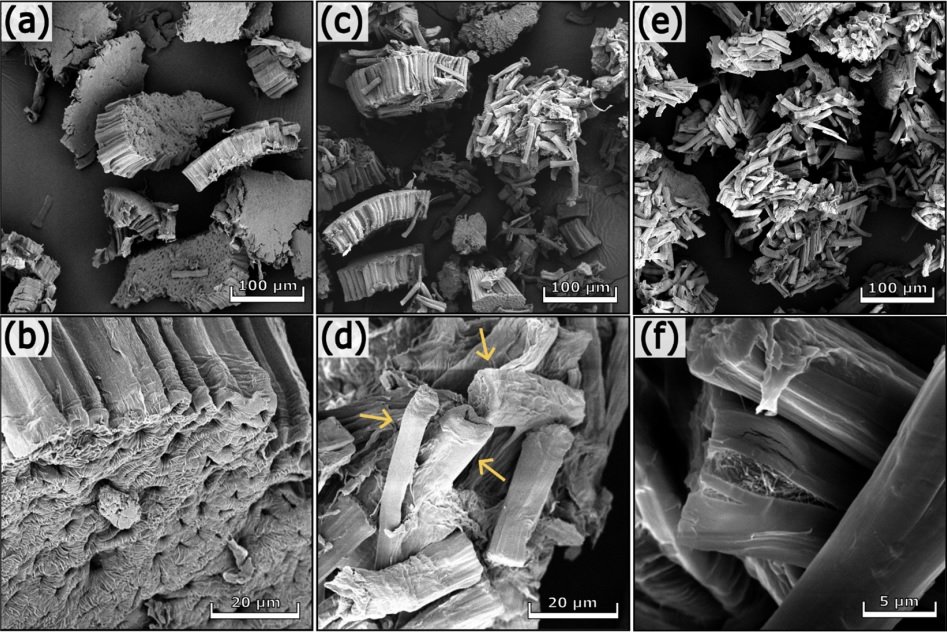
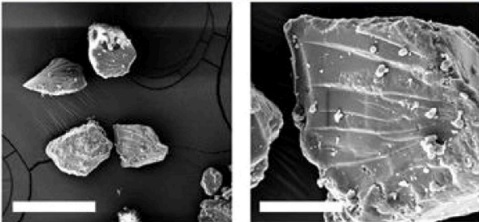
In a research published in the ACS publications, 2026, licensed under CC-BY 4.0, the photoelectrochemical (PEC) performance of the Zr-based MOF, PCN-222 is optimized by substitution of Ti for Zr nodes, pore encapsulation with phosphotungstic acid (PTA), and the integration of charge-selective interlayers (e.g., TiO2 or NiOx).
This structural tuning successfully inverts the intrinsic photocathodic behavior of pristine PCN-222 (Zr) to a highly efficient photoanodic response when Ti is introduced. The subsequent encapsulation of PTA further boosts the anodic photocurrent through its electrocatalytic functions. The thorough mechanistic analysis of charge dynamics is performed by comprehensive characterizations, such as FE-SEM, EDX, etc.
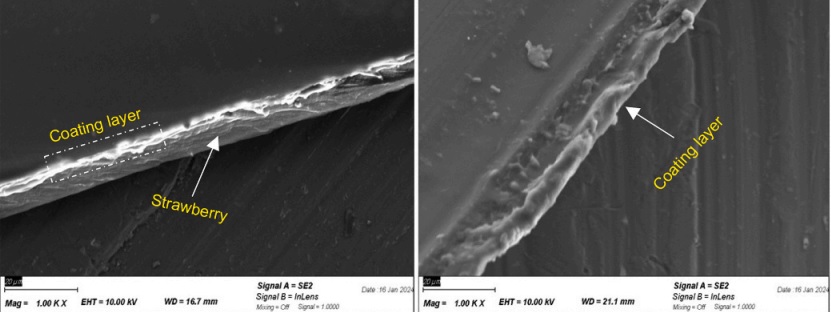
Metal coating before FE-SEM analysis is often critical in MOF and photocatalyst characterization. The homogeneity, film thickness, and surface morphology of the soft, organic-inorganic PCN-222 is measured after coating a conductive thin Au film (10 nm) using a Vac Coat sputtering device (model DSCT) to enhance surface conductivity and minimize charge accumulation during SEM analysis.

Gold/Palladium Thin Film Coating of Neuronal Samples by DSCT for BSD and EM Imaging
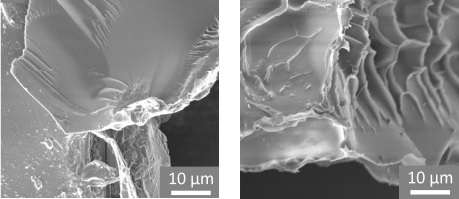
A recent study used high-resolution 3D electron microscopy to analyze myelinated axons in the peripheral nervous system. The results show that the endoplasmic reticulum- a key neuronal organelle- and mitochondria increase in number together as axon size grows, while their individual sizes remain independently regulated.
The samples were characterized through Backscattering Diffraction (BSD) analysis and high-resolution electron microscopy imaging, which relied critically on optimized sample preparation and proper surface conductivity. Therefore, resin-embedded samples were sputter-coated with a thin conductive Au/Pd layer using the Vac Coat DSCT sputter coater prior to SBF-SEM imaging. Coating a thin film of a conductive substance ensures charge dissipation, enhanced image contrast, and stable cutting–imaging cycles during long 3D acquisitions. This preparation step enabled imaging of delicate axonal membranes and organelle contact sites without charging artifacts.
Overall, the work highlights how advanced EM sample preparation, supported by precision sputter coating with Vac Coat SEM coaters, is essential for extracting quantitative, biologically meaningful insights from large-volume 3D electron microscopy datasets.

Reliable SEM Imaging in Occupational Safety Research Enabled by DCT, Vac Coat’s Precision Carbon Coating System
In a recent study performed by researchers in the Republic of Korea, the occupational safety of healthcare workers against the risk of oxaliplatin exposure was evaluated. This might happen during novel heated CO₂ pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC) and hydrothermal PIPAC (HPIPAC) using oxaliplatin. Researchers compared air, surface, and biological contamination levels between conventional intravenous (IV), PIPAC, and HPIPAC methods. Most air samples showed no detectable platinum, indicating minimal inhalation risk. However, surface contamination—particularly on gloves and surgical tools—highlighted the need for strict cleaning and protective procedures.
For microscopic and elemental analysis, air filter samples were examined using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). To ensure accurate imaging and prevent charging under the electron beam, all samples were coated with a thin carbon layer by high vacuumcarbon coater model, DCT. This coating step was essential to achieve clear surface morphology and reliable elemental readings, as uncoated samples can distort signals or cause beam instability.
The coating process was carried out using the Turbo-pumped Desk Carbon Coater from Vac Coat Ltd. (London, UK), which offers fast deposition, uniform coating on the membrane filters. The high-quality carbon film produced by this coater allowed the researchers to visualize nanoparticles and confirm that no platinum particles were present, supporting the study’s conclusion that airborne exposure was negligible.
By combining Vac Coat’s precision coating technology with JEOL FE-SEM and EDX systems, the team achieved highly reproducible and contamination-free imaging result, which demonstrates that reliable coating for electron microscope sample preparation is a critical part of investigating micro/nano-size particles.

Gold Coating of Biomaterials by DSCR for FESEM Imaging
Researchers from the Kiel University, Germany, have investigated a sustainable approach to convert sweet cherry stalk residue (SCS) – a low-cost agricultural by-product – into cellulose nanocrystals (CNC), using ultrasound-assisted acid hydrolysis (UAAH) and insect oil/water Pickering emulsions.
Gold sputter deposition played an important role in microscopic imaging of the samples. Before imaging the samples with a field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), all dried cellulose and CNC samples were coated with a thin layer of gold using the Vac Coat vacuum sputter coater, DSCR. This conductive coating prevents the surface from being charged by the incident electron beam in FESEM imaging, hence increases image resolution and quality, thereby allowing for accurate visualization of the morphological transformation from raw cherry stem fibers to delignified cellulose and ultimately to nanocrystalline cellulose.

Pt Coated Double-Network Hydrogels by DSR1 Prepared for SEM Imaging
This structure provides a cell-friendly environment for umbilical cord–derived mesenchymal stem cells (ucMSCs). This study included both in vitro cellular experiments and in vivo testing using a rat sciatic nerve injury model, where the DN hydrogel demonstrated superior mechanical properties and higher cell viability compared to the single-network (SN) counterpart.
To enable reliable measurement of pore-wall thickness and reduce imaging noise during electron microscopy, freeze-dried hydrogel samples were coated with a thin film (9 nm) of platinum, using DSR1 sputter coater designed by Vac Coat Ltd. This metallic coating improved microstructural image clarity and contrast and prevented surface charging during electron-beam imaging.

DSCT SEM Coater for Investigation of Zeolite Porous Structure
The DSCT sputter and carbon coater has aided a recent study by an Italian research group to investigate heavy metal ions uptake by zeolite architectures with hierarchical porosity. The conventional zeolite frameworks possess microporous structure that limit the metal ion adsorption efficiency.
The researchers have developed zeolites with at least two interconnected classes of pores of different sizes, 2-50 nm, by a top-down desilication treatment. This approach enhances accessible active sites, called Brønsted acid cites, through the internal surface area of the material, which is critical for Cu²⁺ and Co²⁺ cation exchange, without extreme change in the specific surface area.
In this study, the DSCT SEM coater has been used to coat the zeolite porous structures with a 30 nm platinum thin film to increase the sample conductivity and prevent the insulating particles from becoming electronically charged under the electron beam.

Vac Coat Desk Thermal Evaporator for Skyrmion Characterisations
In a recent research, Vac Coat thermal evaporator have paved the way for studying strain-induced formation and stabilization of skyrmion lattices in Fe₃GaTe₂ (FGaT) nanosheets, a room-temperature two-dimensional van der Waals ferromagnet. These nanosheets are transferred onto flexible PET substrates after thermal annealing at 323 K and incurred uniaxial inhomogeneous strain.
By stretching the flexible substrate, the samples suffered inhomogeneous strain that led to skyrmion formation visualised through magnetic force microscopy (MFM). By increasing the strain to 0.80%, highly ordered and robust skyrmion lattice is observed even after 2000 test cycles.
Vac Coat DTT (Desk Thermal Evaporator) was used to fabricate Hall bar electrodes and by thermal evaporation deposition of chromium and gold layers, ensuring precise electrical contacts for transport and resistance measurements in this research.
These findings provide a deeper comprehension on the magnetic manipulation in 2D materials and developing flexible, low-power spintronic devices for future data storage and sensing applications.

Vac Coat DSCT Sputter Coater Used In Sample Preparation For SBF-SEM
The novel Serial Block Face Scanning Electron Microscopy (SBF-SEM) is a 3D imaging techniques useful in studying biological samples. In a recent study, utilizing SBF-SEM method for 3D imaging of peripheral nerves and dorsal root ganglia (DRG) is scrutinized through different sample preparation techniques, the gold standard method, automated standard transmission electron microscopy (TEM) preparation, and automated uranyl-free en bloc preparation, with the latter generating the high-quality imaging of peripheral nerves.
The DSCT Vac Coat sputter and carbon coater was used during the sample preparation phase for SBF-SEM to enhance surface conductivity and minimize charge buildup on non-conductive resin-embedded biological samples.
The samples, once trimmed and mounted, were coated with a thin film (on the order of a few nanometers) of gold-palladium through sputtering deposition technique by DSCT coating system to allow stable, high-quality SEM imaging.

DSR1 Sputter Coater in Biomass SEM Imaging
In a research by a group in University of Torino, the chemical extraction of cellulose from soybean hulls and hemp waste using alternating alkaline (2% NaOH) and acidic (1 M HCl) treatments was investigated. SEM structural observations, along with data from FTIR, elemental analysis, TGA, and XRD, confirmed an increase in crystallinity (up to 87% for soybean) and effective removal of amorphous materials and minerals.
A key component in the characterization phase of this process is the Vac Coat DSR1 sputter coater, which plays a crucial role in the sample preparation step before Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) analysis. Specifically, SEM samples were coated with a thin layer of gold using the Vac Coat DSR1. Since cellulose, as a biomass, is a non-conductive material, this gold coating is essential to prevent charging under the electron beam, improve image clarity, and enhance the image resolution.
High-quality, detailed SEM imaging of the samples, enabled by the Vac Coat DSR1 sputter coater, revealed significant morphological transformations in the fibers, including surface roughening, disaggregation of fiber bundles, and the emergence of individual cellulose fibers with increased crystallinity, throughout the chemical treatment process.
Thus, the Vac Coat DSR1 was instrumental in visually confirming the purification and structural refinement of cellulose fibers throughout the experimental workflow.

Platinum Coated Hydrogels by DSR1 for SEM Imaging
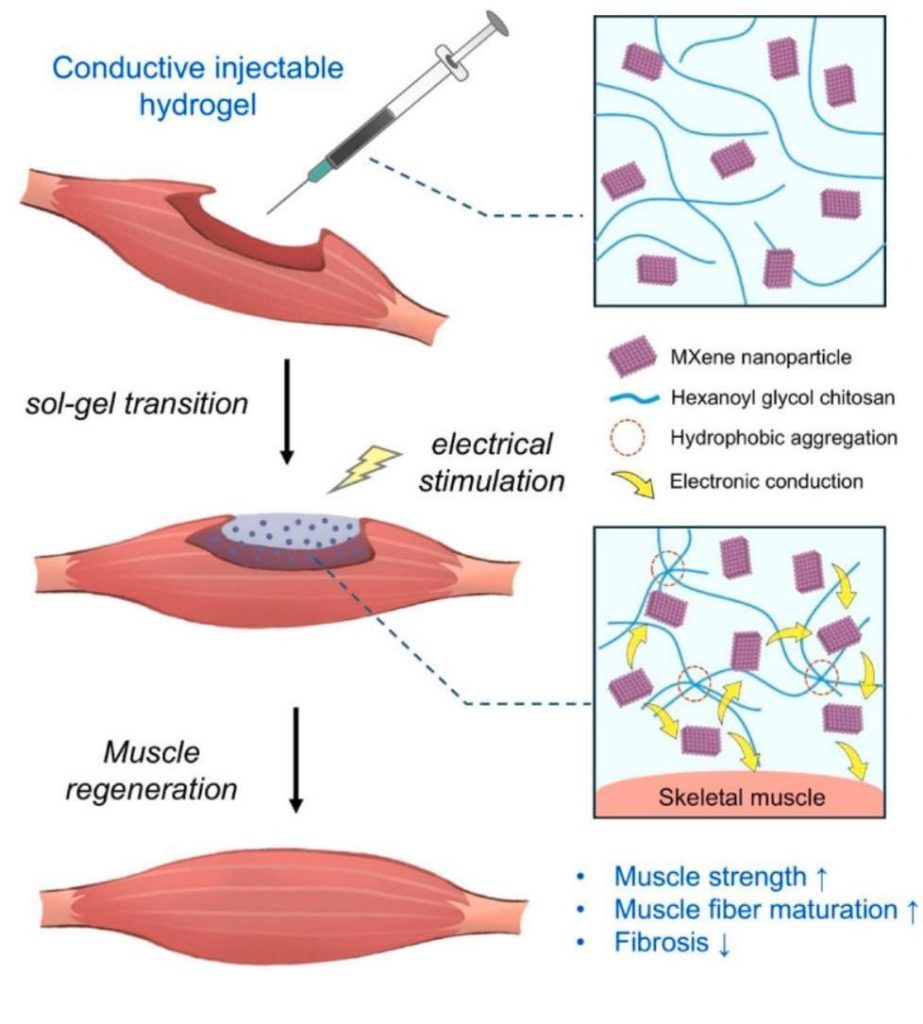
This study investigates a novel injectable conductive hydrogel composed of MXene nanoparticles (Ti₃C₂Tₓ) and hexanoyl glycol chitosan (HGC) as a functional biomaterial for treating volumetric muscle loss (VML). The hydrogel is designed to mimic the physical and electrical properties of skeletal muscle tissue. It supports regeneration by enhancing myogenesis and enabling electrical stimulation (ES) for functional recovery.
Hydrogels are three-dimensional networks of hydrophilic polymers that can help regeneration and repair of various tissues with structural and mechanical properties similar to those of the native muscle tissues. The synthesized hydrogel in this research demonstrated injectable, thermo-responsive properties, as well as high electrical conductivity, and proper biocompatibility, which results in substantial improvement in muscle mass and strength recovery in mouse VML models, especially when combined with ES.
The Vac Coat DSR1 sputter coater was specifically used for platinum coating the lyophilized hydrogel samples prior to SEM imaging (Scanning Electron Microscopy). This coating is essential to prevent sample charging under the electron beam and achieve enhanced imaging resolution and contrast, which allow accurate visualization of the microstructure and porosity of the hydrogels.
Vac Coat sputter coaters, including DSR1, enable high-quality SEM imaging, playing a critical role in characterizing the internal architecture of micro/nano structures. In this case, thorough SEM images of hydrogels helped to correlate microstructural properties with mechanical performance and cell interaction.

DSR1 Magnetron Sputter Coater Used In FE-SEM Imaging Of Recycling Effect On Polypropylene
Vac Coat sputter coater DSR1 is involved in a new study that explores the feasibility of using recycled post-consumer polypropylene (PP) compounds in the automotive industry, focusing on their morphological, thermal, and mechanical properties, and their behavior under UV aging.
The research highlights the growing concern over plastic waste management in the automotive sector and the importance of sustainable solutions like mechanical recycling. It compares post-consumer recycled (PCR) PP with virgin PP to assess the impact of recycling on material properties and the potential for replacing fossil-based polymers in vehicles.
The Vac Coat DSR1 sputter coater was used in the preparation of samples for Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM) analysis. This low vacuum magnetron sputter coater was used to apply a 12 nm gold layer to cryogenically fractured samples, a necessary step in the metallization process before SEM examination. In a second phase of the analysis, samples were coated with a 6 nm gold layer with DSR1 sputtering system. This coating enhances the conductivity of the samples, allowing for high-resolution imaging of the material’s morphology.

Electron Microscopy Imaging of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensors Coated by Vac Coat DSCR SEM Coater
Recently, researchers have developed molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)-based electrochemical sensors to track vitamin B12 (VB12) released from spray-dried microcapsules during in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion. The researchers used o-aminophenol (AP)-based MIP films for electrochemical sensing, demonstrating their effectiveness in detecting VB12 with high sensitivity and selectivity.
The Vac Coat Desk Sputter and Carbon Coater (DSCR) was used in the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis to prepare the sensor surfaces for imaging. A Gold coating was applied to the electrode surfaces and microcapsules before SEM imaging to enhance conductivity and improve image resolution. This sample preparation step ensured clearer morphological analysis of both the MIP films and the spray-dried VB12 microcapsules, allowing for accurate surface characterization.
TEM imaging of the powdered sample was performed on a copper grid with a carbon lacey support.
The VB12 was encapsulated using complex coacervation-based emulsions and the electro-MIP sensor exhibited high selectivity and stability, and is cheaper, portable, and easier to use in comparison to other methods like HPLC and UV-Vis spectroscopy.

Vac Coat DSR1 Sputter Coater for Solar Cell Fabrication
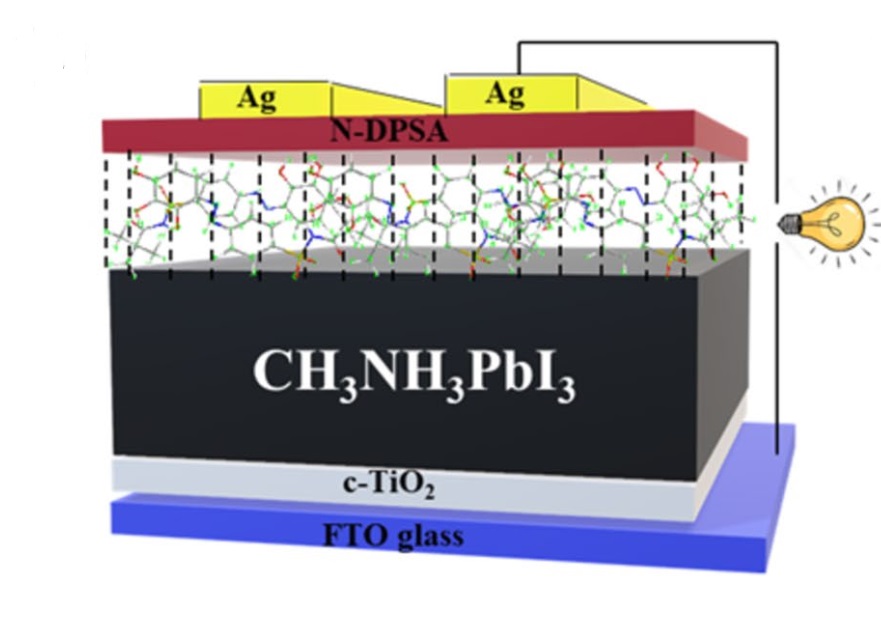
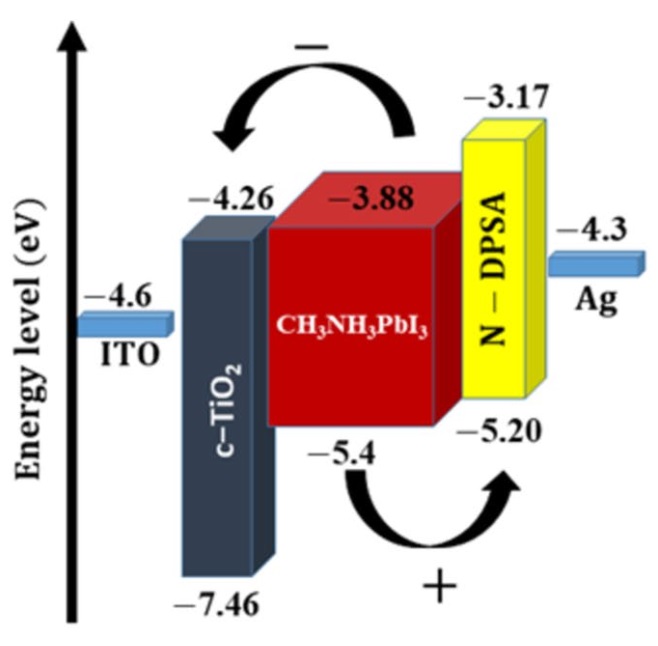
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are the new generation of solar cell that have gain tremendous attention, give rise to nearly 35% efficiency. A range of hole transport materials (HTMs) have been investigated to achieve the best result. In a recent study, novel pyrogallol-sulfonamide derivatives, particularly N-DPSA, were synthesized utilizing a molecular hybridization approach for use as HTMs in PSCs.
Hall-effect measurements demonstrated significant hole mobility and conductivity values for N-DPSA, indicating its potential as a p-type semiconductor with a direct optical energy gap of 2. 03 eV.
The synthesis process was noted for its simplicity and low cost, with N-DPSA achieving a power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 7.3% under optimal conditions.
How DSR1 Helped Solar Cell Fabrication?
The device fabrication was completed with deposition of back contact electrodes with DSR1 low vacuum sputter coater. The back contacts were formed by deposition of 80 nm Ag on top of N-DPSA layer as HTM layer.
This novel pyrogallol-sulfonamide hybrid presents promising characteristics for the effective development of low-cost, efficient HTMs in renewable energy sources. Future work will focus on material enhancements and interface optimization to maximize the performance potential of N-DPSA in practical applications.

SEM Imaging of Encapsulated Olive Mill Wastewater Gold Coated by DSCR Sputter and Carbon Coater System
A research group at Kiel University has investigated the olive mill wastewater (OMWW) inclusion complex with hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) to optimize its antioxidant properties and thermal stability for use in pharmaceutical products and fortified foods.
OMWW is a byproduct in olive oil extraction process that has harmful effects on the environment duo to sulfur dioxide emission, though, it is a powerful antioxidant and demonstrates antimicrobial, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory properties which is useful in applications like wound healing patches or natural food packaging. However, it suffers from shortcomings like high sensitivity to thermal treatments and low bioavailability because of its hydrophobic structure.
In this study the HP-β-CD cone-shaped structures are employed to encapsulate OMWW phenolics due to their amphipathic (Hydrophobic interior cavity and hydrophilic exterior surface) structure as a host-guest complex (With different molar ratios), to achieve a stable structure that can replace synthetic antioxidants with natural alternatives which aligns with consumer preferences.
The structure of these complex inclusions have been studied through electron microscope imaging. The samples were undergone a preparation step for scanning electron microscopy through deposition of a thin film of gold by sputtering process using DSCR sputter and carbon coater machine. The DSCR sputter coater is one of the versatile low vacuum SEM coaters made by Vac Coat Ltd. that is widely used for SEM sample preparation and contacting.

Vac Coat DSCR Coater Used in SEM Imaging Biological Samples
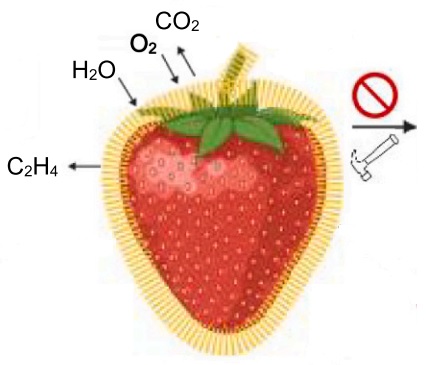
Food product preservation is a vast research field in the food industry. Edible coatings are one of the best approaches to maintain food quality and extend its shelf-life. They can be engineered as different emulsion types, such as oil-in-water (O/W) NEs to encapsulate and deliver fat-soluble vitamins, flavors, antioxidants, and bio-preservatives like essential oils (EOs).
In a research conducted at Kiel University, Germany, eryngo (Eryngium caucasicum Trautv) EO-based NEs have been studied to preserve food products, strawberry in this case. An insect protein (LMPI) was used to stabilize eryngo EO-loaded NEs in this study.
Samples were initially sputtered with a gold coating by Vac Coat Desk Sputter and Carbon Coater DSCR in an Ar plasma medium to enhance conductivity and obtain SEM micrographs with a higher resolution.

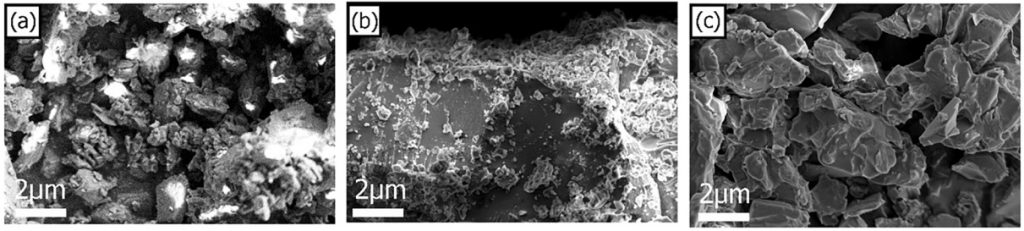
Gold-Coated Mycelium-Based Bio-Composites For FE-SEM Imaging
Recently, researchers from Colombia have investigated mycelium-based bio-composites for sustainable development of biodegradable materials. The structure of these materials was characterized by Field Emission Scanning Electron Microcopy (FE-SEM), which were prepared through 3-nm gold sputter coating prior to electron microscopy.
The mycelium-based bio-composites are produced through solid-state fermentation (SSF) of agro-industrial wastes that serve as nutrients and support for the fungi vegetative body, facilitating mycelium spread as it grows and branches.
These bio-composites have many advantages like low energy consumption during manufacturing, biodegradability, cost-effectiveness, high specific stiffness, and lower environmental impacts compared to other alternatives, together with high acoustic and thermal absorption, high impact resistance, and low density, which allows for medical applications, as well as applications in construction, packaging, vehicle parts, and electronics.
In this paper, the morphology of different agro-waste samples, like sugarcane bagasse (SCB) wet dust (a second-generation waste from the paper industry), peach palm fruit (PPF) peel flour made from the outer layer of the fruit, and a mixture of them (MIX) were examined for mycelium coverage and degradation by FE-SEM. The samples were prepared by deposition of a thin film of gold (3 nm) by DSR1 desk sputter coater (manufactured by Vac Coat Ltd.) to enhance their electrical conductivity, hence achieving magnifications of 300 and 20 000 under 3 kV accelerating voltage.
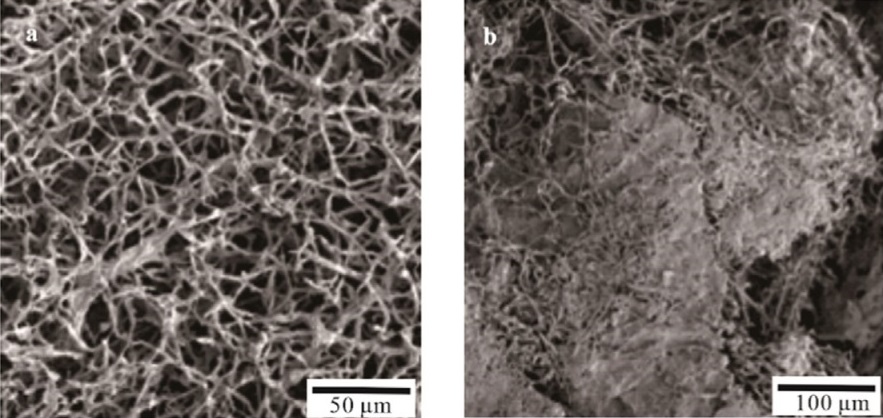
The images in Figure 1 show the formation of mycelium “Fungal Skin” covering the surface area of the bio-composites, responsible for the their prolonged deformation without failure and enhanced mechanical and physical behavior.

Triboelectric Nanogenerator Creation Using DSR1 Sputter Coater
Researchers from Cambridge University have produced contact-separation mode triboelectric nanogenerators (CS-TENGs) by sputter coating a 100 nm gold thin film on nylon 6 film (0.1 cm thickness) using DSR1 Sputter Coater.
In this research, self-healable PDMS (SH-PDMS) was coated with Ecoflex elastomer to preserve the self-healable and tribonagative properties of the material. Nylon 6 film was employed as the tribopositive material. These contact-separation triboelectric layers were contacted with a thin film of Copper (Cu) and gold (Au) as electrode layers, respectively. The gold thin film deposition is executed by sputtering method utilizing DSR1 SEM Sputter Coater, in which the high-energy plasma ions in the vacuum chamber collide with the Au target and sputter them to coat the substrate.
Ecoflex/SH-PDMS films with a silicon−oxygen chemical backbone (−Si−O−) show negative triboelectric with flexibility and robust mechanical properties.
Electrostatic induction during periodic contact and separation is the main operational principle of the CS-TENG devices made from Ecoflex/SH-PDMS/Cu and nylon 6/Au layers. An interface dipole layer is created on each material/electrode junction by pressing the two layers and contact electrification. By releasing the layers, an output signal is generated by the flow of electrons in the external circuit due to the electrostatic induction. A reverse current flow will happen during the next pressing step. Consequently, alternating current signals are produced by continuous periodic contact separation of the two layers.
DSR1 is a low vacuum, rotary-pumped sputter coater that is suitable for the creation of noble metal coatings. Vac Coat also offers other coating systems, such as high vacuum sputter coaters, DST1, DST3, and DST2-TG, along with low and high vacuum carbon coaters, DCR and DCT, and hybrid coaters that combine several coating techniques in one device, like DSCR, DSCT, and DSCT-T.

SEM imaging of functionalized membranes for hepatitis A virus capture gold coated by Vac Coat DSCR
The Hepatitis A virus (HAV) is a highly stable virus that can be transmitted through contaminated water, so applying a safe method like physical removing of HAV through membrane filtration is under investigation.
In this research, membranes of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and polyethersulfone (PES) have been functionalized by chitosan hydrophilic surface modifications to immobilize HAV-specific epitope-imprinted polymers (eIPs), which leads to removal of HAV traces from drinking water. These bio-selective membranes nearly removed 99.99 % of HAVs from water samples, showing reliable HAV removal capabilities potential for drinking water purification.
The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) imaging of the specimens revealed that morphology of chitosan functionalized PVDF and PES smoothed by reducing porosity, while their surface structure changed after eIP immobilization, resulting in increased surface anomalies.
The SEM sample prepared through deposition of a noble metal thin film to enhance samples’ electrical conductivity. Samples were sputter coated with a gold coating using Vac Coat Low Vacuum Desk Sputter and carbon Coater DSCR in an Argon plasma environment.

SEM study of applied antibacterial properties of the vehicle textile materials with Vac Coat DSR1 SEM coater
Researchers of the University of Turin, in Italy, have investigated durability of various antibacterial treatments to seek novel solutions to improve the performance of textile materials for the automotive industry against two model microorganisms, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureu. Consequently, the effect of mechanical, thermal, and solar aging on the antibacterial properties has been studied.
The specimens have gone through several characterization techniques like contact angle measurements and scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis to investigate the surface hydrophobicity and morphology of the samples before and after aging. Prior to the SEM analysis, the samples were placed on a metal stub and coated with a 3 nm gold layer by Vac Coat DSR1 sputter coater.
DSR1 sputter coater is a precise low vacuum SEM coater that is ideal for deposition of noble metal thin films by sputtering technique, which is a physical vapor deposition method.
The results show that the antibacterial performance was not diminished by mechanical or thermal aging processes, although, UV aging caused the most severe surface alterations and a reduction in antibacterial activity.

Cardiac Troponin I Sensors Gold Sputtered By Vac Coat DSCR for SEM Analysis
Researchers at Technical University of Berlin and Kiel University have studied dopamine (DA) electro polymerization and synthesis with nanomaterials like gold nanoparticles (AuNP) and graphene quantum dots (GQD) to develop cardiac troponin I (cTnI) sensors. These structures were gold coated with Vac Coat DSCR SEM coater for further analysis through Scanning Electron Microscopy.
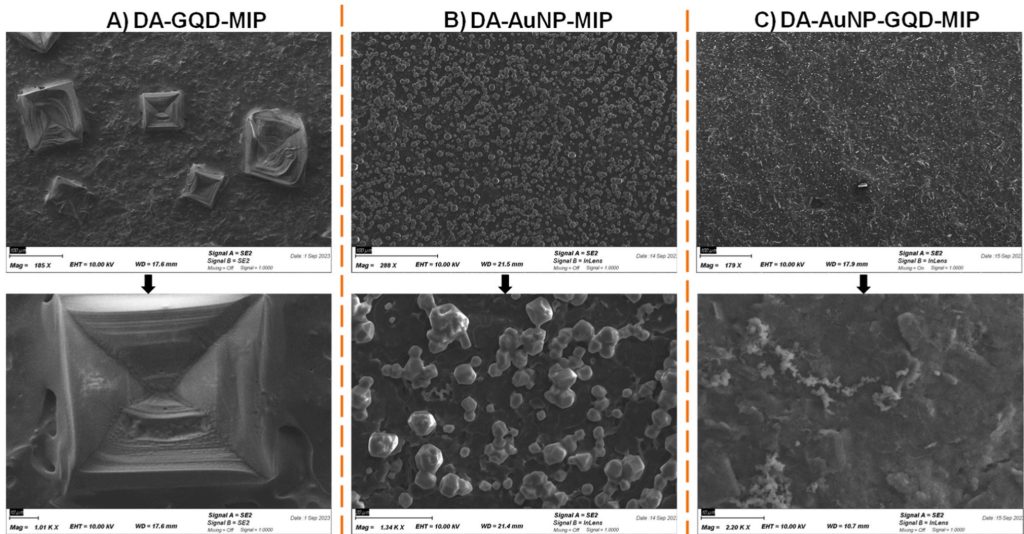
The cardiac troponin I (cTnI) can be used as a circulating biomarker that is associated with coronary artery diseases (CAD) and an interpreter of cardiovascular disease (CVD). The aim of this research is to develop ultrasensitive, highly selective, cost-effective cTnI sensors with evaluating their sensitivity, selectivity, and specificity profiles. Henceforth, three distinct electrochemical sensors were synthesized based on molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) named (DA-AuNP-MIP, DA-GQD-MIP, and DA-AuNP-GQD-MIP) for detecting cTnI.
Molecularly imprinted polymers, serving as plastic antibodies, show remarkable affinity, specificity, and selectivity for the target molecules. The sensitivity of MIPs can be improved by integration of smart nanomaterials, such as gold nanoparticles (AuNP), graphene quantum dots (GQD) or a combination of both, into MIPs through electrochemical processes.
The surface morphology of the samples was studied using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). To make the samples conductive for high-quality SEM imaging, they were coated with a thin film of gold by sputtering deposition with Vac Coat Desk Sputter and carbon Coater DSCR (I = 10 mA, time = 30 seconds) in an argon plasma environment. The SEM images are shown in Figure 1.
Vac Coat offers SEM coaters supplied with Quartz crystal thickness sensors for precise control over deposited film thickness. Low vacuum sputter coater DSR1 is an ideal sputtering coater for swift noble metal thin films deposition. Low vacuum carbon coater, DCR, and combined low vacuum sputter and carbon coater DSCR provides conductive coatings for SEM sample preparation. High vacuum sputter coater DST1, carbon coater, DCT, and combined sputter and carbon coater, DSCT, are perfect SEM coaters for deposition of oxidizing metal films, like tungsten, with a small grain size for high-resolution electron microscopy imaging. DTE and DTT thermal evaporators are also suitable candidates for surface metallization of insulating SEM specimen.

SEM imaging of DSR1 platinum-coated nerve guidance conduit (NGC) Hydrogels
In recent research on finding a new material working as a nerve guidance conduit (NGC) to repair injured or diseased peripheral nerves, double network hydrogels made from 1% alginate and 15% gelatin have shown promising results. The SEM images of the platinum-coated hydrogels with Vac Coat DSR1 SEM coater display 6.5 times thicker pore walls for double network (DN) versus single network (SN) structure.
Y. Lee group at Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) have shown that the mechanically strong, degradable, and biocompatible DN alginate/gelatin hydrogels, with enhanced performance through gamma irradiation, can serve as an innovative platform for biomedical applications as implantable tissue constructs and peripheral nerve regeneration.
The hydrogels were freeze-dried and sputter coated with a thin film of platinum with a thickness of 9 nm to get prepared for Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). The sputtering process was performed by DSR1 Vac Coat low vacuum sputter coater. The SEM images indicated that both DN and SN NGCs possessed the porous structures of typical hydrogels with nearly similar pore sizes for permitting nutrient and waste transport (Figure 1). However, the DN hydrogel network was much denser than the SN one, with DN pore walls approximately 6.5 times thicker than those in the SN hydrogels.

Gold coating Dextrin-based nanosponges by DSR1 SEM coater
Researcher at University of Siena in Italy have used Vac Coat DSR1 sputter coater to study surface structure of dextrin-based adsorbent biopolymers used for water treatment.
The environmental safety of dextrin-based nanosponges, like cyclodextrin (CD) and maltodextrin (MD), is investigated in this research. These biopolymer nanosponges have shown promising adsorption properties, which benefit biomedical applications, cosmetics and food industry, as well as water remediation as adsorbent materials for the removal of toxic chemicals that will lead to their release into the natural environment.
The surface structure of nanosponges were studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) after metallization of the specimens’ surface with a 12 nm thin film of gold by Vac Coat DSR1 sputter coater as a sample preparation step. DSR1 is a desk magnetron sputter coater with a single cathode equipped with a rotary pump that is suitable for deposition of noble metals, mainly used for SEM sample preparation. The SEM characterization displayed smooth external surfaces and the absence of macro-porosity, as shown below.
The results revealed that exposure to both aquatic organisms and plants does not cause harm even at high concentrations of dextrin-based nanosponges and can be extended to all dextrin-based polymers with similar formulation and exposure levels in the range of mg/mL.

Gold coating of maltodextrin-based cross-linked polymers by Vac Coat SEM coater DSR1
Researchers at University of Turin have developed cross-linked bio-derived cationic polymers from maltodextrin product to measure their water absorption capacity and water remediation capability as gel formation and nitrate, sulfate, and phosphate removal tests.
These polymers were comprehensively characterized via FTIR-ATR, TGA, DSC, XRD, SEM, elemental analysis, and zeta-potential measurements, to investigate their composition, and structure, along with other mechanical and chemical properties. For SEM imaging of the polymers, they were coated with a gold thin film of 12 nm with Vac Coat Desk Sputter Coater DSR1, and the SEM imaging of the polymers before and after the water adsorption are as follows:
Subsequently, the water absorption capacity of the cross-linked polymers was measured ranging from 800% to 1500%, and water remediation tests for removal of common pollutants like nitrate, sulfate, and phosphate showed high sorption rates, with 80% of nitrates, over 90% of sulfates, and total phosphates removal.

FE-SEM characterization of neural cells with Vac Coat Sputter and Carbon coater
In a recent study, the role of the Indian herb Bacopa monnieri in treating oxidative stress in neuronal cells has been investigated through electron microscopy imaging. This study suggests that Bacopa monnieri and its active compounds could be used as a new drug for the prevention and treatment of oxidative stress-related neurodegenerative diseases as a natural remedy.
This article has investigated the therapeutic potential and molecular complexities of Bacopa monnieri, recognized for its neuroprotective and cognitive advantages, in treating neurological disorders and brain damage influenced by oxidative stress.
The morphological features of the cells in response to the methanolic extract of Bacopa monnieri (BME) and its active component, Bacoside-A, checked through FE-SEM characterization, show enhanced neuronal cell protection against oxidative stress as in neurodegenerative diseases. The neuronal cells grown over coverslips underwent the required treatments and then were mounted on carbon tape which was pasted on the sample holder stage and prepared for observation after gold coating with Vac Coat sputter and carbon coater, DSCR. The SEM observation was carried out using a Zeiss high-resolution microscope.
The below figures show the morphology of neural HT-22 cells pre-treated with BME in contrast to the non-treated cells in the presence of oxidative stress (H2O2 treatment), comparable to the control cells (Yellow arrows show the damaged membrane by oxidative stress). Maximum protection was obtained in both BME (100 µg/ml) and Bacoside-A treated cells, nearly the same as the control cells.

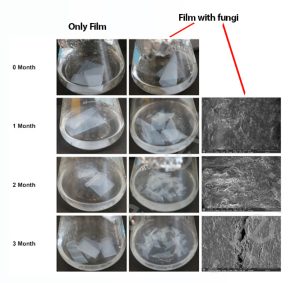
Fungal biodegradation of poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)-polylactic acid-thermoplastic starch based commercial bio-plastic film at ambient conditions
Serious environmental pollution and human health issues can arise due to the enhanced utilization of synthetic plastics manufactured from petroleum resources. Therefore, biodegradable polymers (bio-plastics) made from renewable biological materials like natural aliphatic polyesters poly (lactide) (PLA), poly (butylene adipate-co- terephthalate) (PBAT), etc., are considered as eco-friendly plastics that last for a limited period of time in the environment.
In this paper, Ko et al. have studied the biodegradation of a hydrophilic ternary blend of PBAT-PLA with TPS (thermoplastic starch) by the act of fungal strains at ambient conditions. The surface morphology of the commercial bio-plastic films of PBAT-PLA-TPS was observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The samples were prepared for the SEM analyses by mounting the films on a carbon tape and coating them with a 20 nm thickness platinum film using Vac Coat DSR1 ion sputter coater.
The optical and SEM images of the films with or without the fungal strains at different time intervals are shown below.

Vac Coat DSR1 Utilized in SEM Sample Preparation for Evaluation of βcyclodextrin-based nanosponges Loaded with Budesonide for Pulmonary Delivery
Budesonide (BUD) is a hydrophobic compound utilized to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Francesco Trotta group at Turin University has tried a method to load BUD into the non-toxic and biocompatible βcyclodextrin-based nanosponges (βCD-NS), which resulted in an encapsulation efficiency of 81 ± 5.0 % for the optimized synthesis process.
The morphology of BUD, blank NS, and BUD-loaded NS was studied using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The imaging is conducted using secondary electrons and 10 kV accelerating voltage, with the samples on the aluminum stub. Before SEM analysis, the polymers were coated by Vac Coat Desktop Sputter Coater model DSR1 with 12 nm of gold thin film.
This study demonstrated a longer duration of drug release and absorption from the lungs up to 12 h from BUD-βCD-NS structures, where the initial interval was 2 h for pure BUD. The results of this research suggest the BUD-loaded βCD-NS to be formulated as a dry powder inhaler and offer new insights into the future advancement of βCD-NS as a drug delivery system to achieve controlled release of therapeutic agents via the pulmonary route.

Scanning Electron Imaging of DSR1 Gold Coated Bio-polymers as an Adsorbent of Salicylic Acid in Water
Starch-based bio-adsorbents were successfully observed by SEM, previously prepared through coating a 12 nm gold thin film on the non-conductive bio-based beta-cyclodextrins and maltodextrins. The gold was coated by using the DSR1 SEM coater, a popular Vac Coat ion sputter coater suitable for electron microscopy sample preparation.
The researchers at the University of Turin in Italy worked on the removal of environmentally hazardous salicylic acid in wastewater and surface waters utilizing cross-linked adsorbents derived from starch, like beta-cyclodextrins and maltodextrins. These hydrophilic granular structures showed more than 90% salicylic acid removal with a maximum adsorption capacity of 17 mg.g-1 and recycling up to for cycles.
The samples went through SEM for structural analysis to study the morphology of the biopolymers. The samples were coated with a 12 nm gold thin film by Vac Coat DSR1 low-vacuum sputter coater as an SEM preparation step to enhance the conductivity and reduce charge accumulation on the samples’ surface.
Preparation of the samples for electron microscopy is crucial to improve the imaging results. Vac Coat SEM coaters, such as sputter coaters, carbon coaters, and thermal evaporators are ideal coating devices for coating different conductive layers on electron microscope samples’ surfaces.

Assembly of Colloidal Crystals by Local Heating Induced Through Plasmonic Effect of A Gold Thin Film Deposited by Vac Coat DTT
Leipzig university researchers have coated coverslips with a thin (less than 50 nm) gold film and 5 nm chrome adhesion layer by Vac Coat DTT model to study optically induced 2D and 3D colloidal crystals through dynamic thermofluidic assembly. The results of this research has been published as a journal article in Frontier in Nanotechnology, with the title “Thermofluidic assembly of colloidal crystals” by D. Quinn and F. Cichos in March, 2023.
Crystalline structures as crystalline colloids demonstrate remarkable photonic features, useful in modulation of electromagnetic wave propagation. These structures can be formed in various methods, such as engineering inter-particle interactions, applying external electro-magnetic fields, using optical tweezers, or thermally induced processes, in which local heating of a plasmonic structure like a thin gold film is used to induce a temperature gradient to create/destroy crystalline colloids.
Vac Coat Desktop Thermal Evaporator, DTT, is a high-vacuum coating machine suitable for uniform deposition of different source materials like gold, silver, chrome, etc., by thermal evaporation method. DTT contains three resistive boat/basket source holders, and can be used for simultaneous material deposition if supplied with multiple high-current power supplies (optional).

Study of DSR1 Sputter Coater Gold Coated Polysulfone Membranes Modified by PAA
In the research work done by Plisko T., et al., the polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes were modified by addition of polyacrylic acid to increase their antifouling performance. These insulating membranes were coated with a thin gold layer by DSR1 sputter coater for structural analysis by SEM imaging.
Membrane fouling caused by the sorption of feed mixture particles on the surface and inside pores of the membrane selective layer leads to membrane performance degradation and is a serious problem in membrane technology.
SEM micrographs in “Effect of the Addition of Polyacrylic Acid of Different Molecular Weights to Coagulation Bath on the Structure and Performance of Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes”
Plisko T., et al., modified these ultrafiltration membranes by the addition of polyacrylic acid (PAA) with different molecular weight and concentrations to reach maximum antifouling performance of 136% for 450,000 g·mol−1 PAA.
The influence of PAA molecular weight on different membrane properties, such as surface roughness, water contact angle, zeta potential, the separation, and antifouling performance were experimented. SEM imaging is used to study the insulating structure of these gold coated samples.
It was found that PAA-modified membranes present smaller pore size and porosity, along with greater hydrophilicity and higher values of negative charge of membrane surface.

Vac Coat DSCR Used in SEM Investigation of Amphiphilic Chitosan/18β-Glycyrrhetinic Acid Nanoparticles for Anti-Photoaging Effects
The 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid (NGA) nanocrystals prepared by adsorption of amphiphilic chitosan (ACS) with 10:1 optimal ratio of NGA to ACS was used to prepare ANGA composites, which was utilized to prevent and treat skin photoaging. The results of this article indicated that the NGAs could significantly enhance the photoaging of mouse skin, so the ANGA hydrogel could be used to counteract skin photoaging.
The shape of the ACS coated NGA nanoparticles were studied by SEM characterization after completely drying under vacuum and fixing on a conductive tape. The SEM images of the sample coated with gold for 2 min using Vac Coat DSCR sputter coater, under an excitation voltage of 5 kV, is shown below.

Vac Coat Magnetron Sputter Coater for SEM Investigation of Polymeric Structures
Nowadays, production of biodegradable polymers that do not contribute to microplastic burdens is a worldwide environmental challenge, which is going to be overcome through polymer engineering.
Kim, et al. at University of Waterloo have investigated highly filled thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU) composite systems using a polysaccharide, α-1,3-glucan, as a renewable and sustainable filler material in their research work entitled as “Engineered polysaccharide alpha-1,3-glucan in highly filled thermoplastic polyurethane systems”, which improved the modulus and strength of TPU.
The α-1,3-glucan particles were gold-coated by Vac Coat magnetron sputter coater in order to become observable with scanning electron microscope.
Vac Coat DSR1 is a low-cost SEM coater for deposition of a thin film of non-oxidizing materials, like gold and silver. Vac Coat also offers high-vacuum sputter coater, DST1, and low and high-vacuum carbon coaters, DCR and DCT, for SEM, FESEM and TEM imaging.