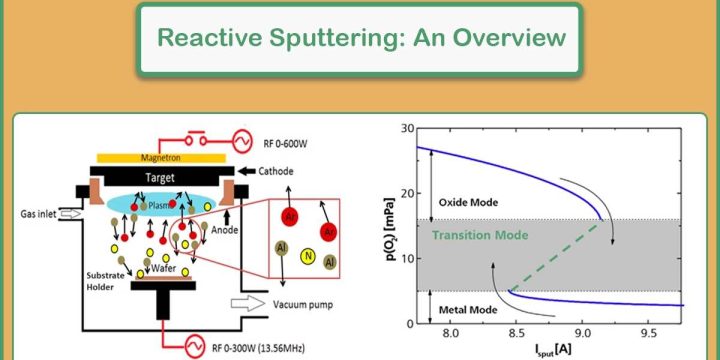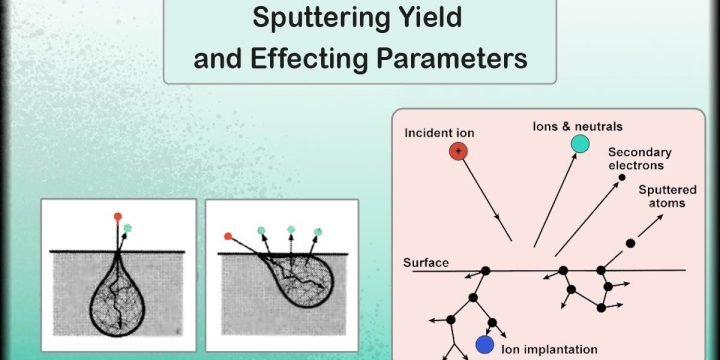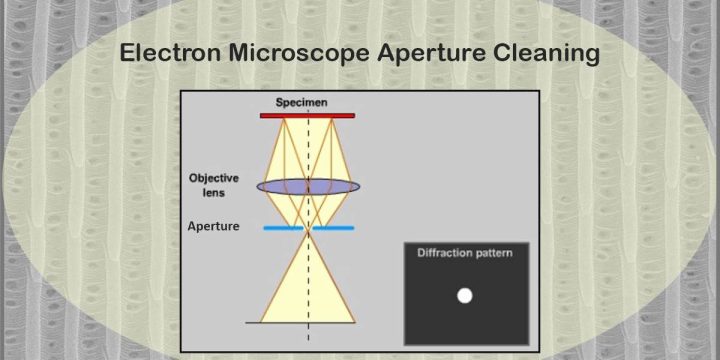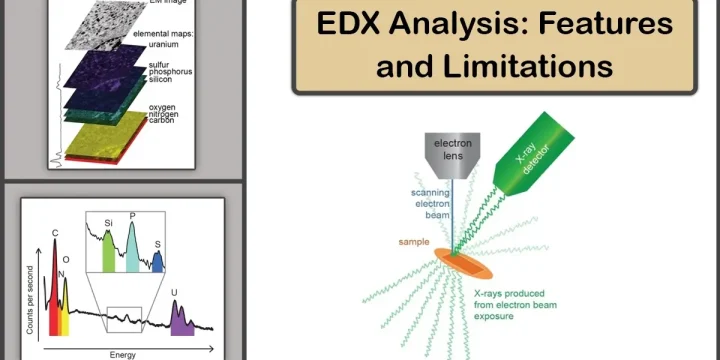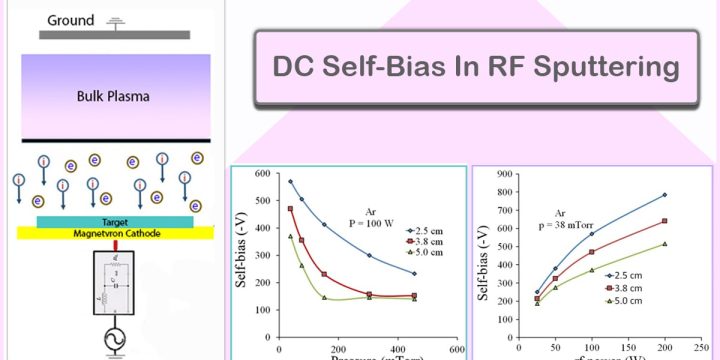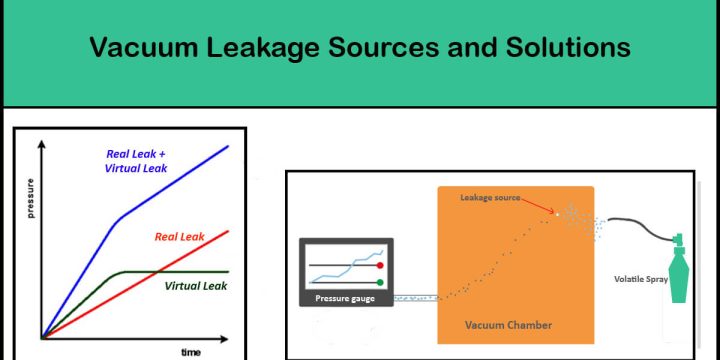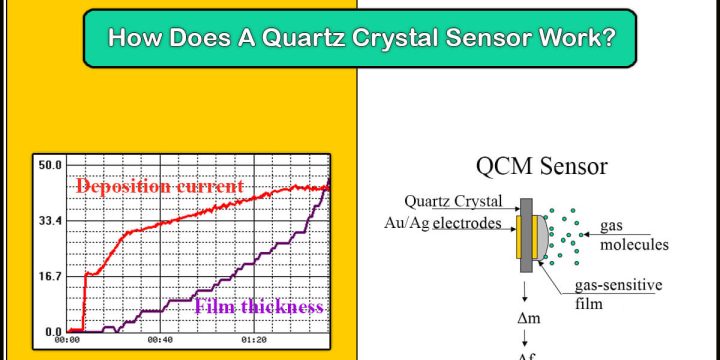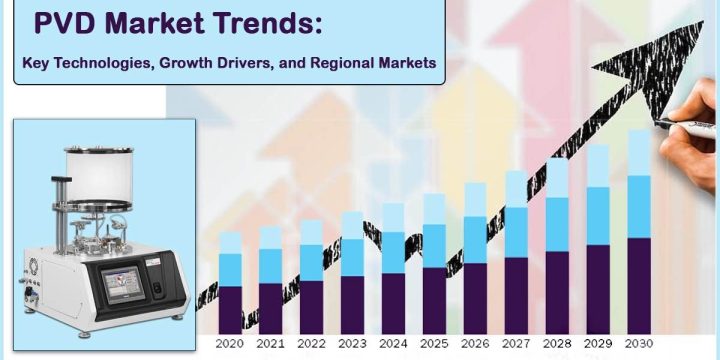
PVD Market: Foundational Technology in High-Tech Manufacturing
[vc_row][vc_column width="3/4"][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width="1/2"][vc_column_text css=""] Physical Vapor Deposition Market Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) represents a cornerstone suite of techniques for depositing thin films of various materials onto substrates, operating under low or high vacuum conditions. Its versatility in handling a wide array of materials (Metals, alloys, ceramics, compounds) and its ability to tailor film properties (Thickness, adhesion, density, stress, electrical and optical characteristics) make it indispensable across numerous high-technology sectors. As we look towards the next decade (2025-2035), PVD market trend is poised for significant growth and technological evolution, driven by relentless innovation cycles in its primary end-use markets. This analysis synthesizes data from recent market reports to provide a comprehensive outlook on the PVD landscape, highlighting key growth drivers, technological advancements, market segmentation, regional dynamics, and strategic considerations relevant from…