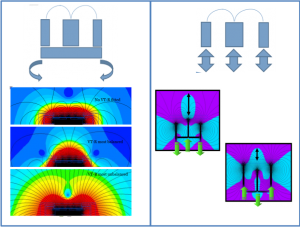
Unbalanced Magnetron Sputtering Cathodes
Balanced and unbalanced magnetron cathodes in sputtering systems have their advantages and disadvantages as mentioned in “balanced and unbalanced magnetron sputtering” article.
What is Unbalanced Magnetron?
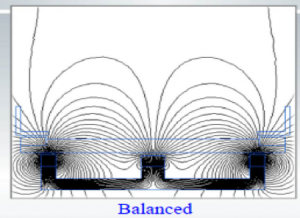
Balanced magnetic fields with magnetic field lines confined around the cathode, limit the charged colliding particles (electron-ions) to the target surface which benefits low friction coatings; whereas in an unbalanced magnetron with some magnetic field lines toward the substrate, the ions bombard the thin film, affecting thin film surface morphology and adhesion to the substrate, suitable for pre-cleaning and hard coatings. Since balanced cathodes are common, here we discuss the unbalanced magnetron cathodes and theirs specifications.

How Much a Magnetic Field is Unbalanced?
To verify the degree of unbalance for a cathode, one can define a geometrical parameter g, which is the ratio of ZBz=0:W1/2; Z is the distance from the target to the position with zero magnetic field (null point), where component B perpendicular to the target changes its direction, and W1/2 is the half width of the target, according to figure 1 [1].
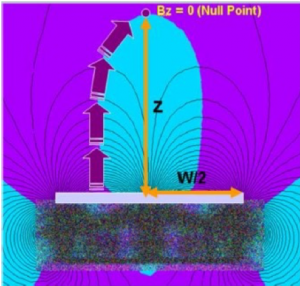
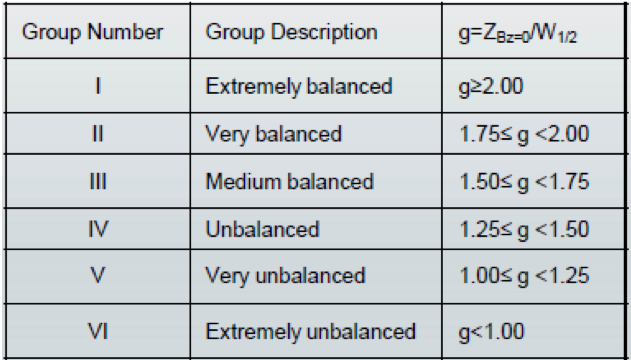
Various unbalance levels can be determined due to different amounts of g, from extremely balanced to extremely unbalanced configuration as defined in table 1, and their schematics is shown in figure 2. These levels of unbalance determine how easy electron-ions can escape the plasma over the target surface and reach the escape point.
Another measure of unbalance magnetic field of a magnetron known as geometrical unbalance coefficient, is defined as KG= ZBz=0:2Rerosion, where Rerosion is erosion zone radius; then for a balanced magnetic field KG values are considered to be greater than 3. The ratio of ion to atom reaching the substrate reduces with increasing KG values as depicted in figure 3 [2].
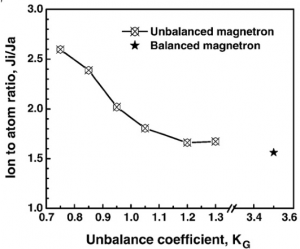
Figure 3. Ion to Atom Ratio for Different KG Coefficients
Industrial Unbalanced Magnetron Cathodes Production
Different companies, like Gencoa Ltd. and Angstrom Sciences produce various unbalanced magnetron cathodes for industrial and research purposes. The plasma produced by an unbalanced magnetron cathode produced by Angstrom Science is shown in figure 4 [4].
As an example, Gencoa Ltd. produces unbalanced magnetron cathodes, in which the magnetic field strength is controlled by moving the inner and outer poles independently or rotate the poles, to vary the field strength over the target and/or change the ion assistance of layer deposition (figure 5).
Magnetron Sputter Coaters
Magnetron cathodes used in Vac coat sputter coaters utilize permanent magnets, which provide uniform and stable magnetic field for enhanced plasma maintenance. In Vac coat, we are able to produce balanced and unbalanced magnetron cathodes to meet our customer demands for various layer deposition conditions.
Vac coat Ltd. designs and manufactures thin film deposition systems using methods like sputtering, thermal evaporation, physical vapor deposition, and pulsed laser deposition. Vaccoat sputter coaters include triple target sputter coater with/without thermal evaporation system (DST3 & DST3-T), single cathode turbo pumped desk sputter coater with different chamber size (DST1-170 & DST1-300), and rotary pumped desk sputter coater (DSR1).
Also, sputter coaters provided with a carbon coater are popular thin film deposition systems for SEM sample preparation (SEM Coaters). These combined systems use rotary pump (DSCR & DSCR-300) or turbomolecular pump (DSCT & DSCT-T) to reach required vacuum levels for layer deposition. For more information, visit the website please.
Related Posts
References
- https://www.gencoa.com/resources/documents/gencoa-magnetic-options-SVC.pdf
- Olaya, J. J., S. E. Rodil, and S. Muhl. Comparative study of niobium nitride coatings deposited by unbalanced and balanced magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 516.23 (2008) 8319-8326.
- Svadkovski, I. V., D. A. Golosov, and S. M. Zavatskiy. “Characterisation parameters for unbalanced magnetron sputtering systems.” Vacuum 68.4 (2002): 283-290.
- https://www.angstromsciences.com/Angstrom_Sciences_Awarded_New_Patent_2001
- https://www.gencoa.com/resources/documents/comparison-balanced-unbalanced-array-designs.pdf