
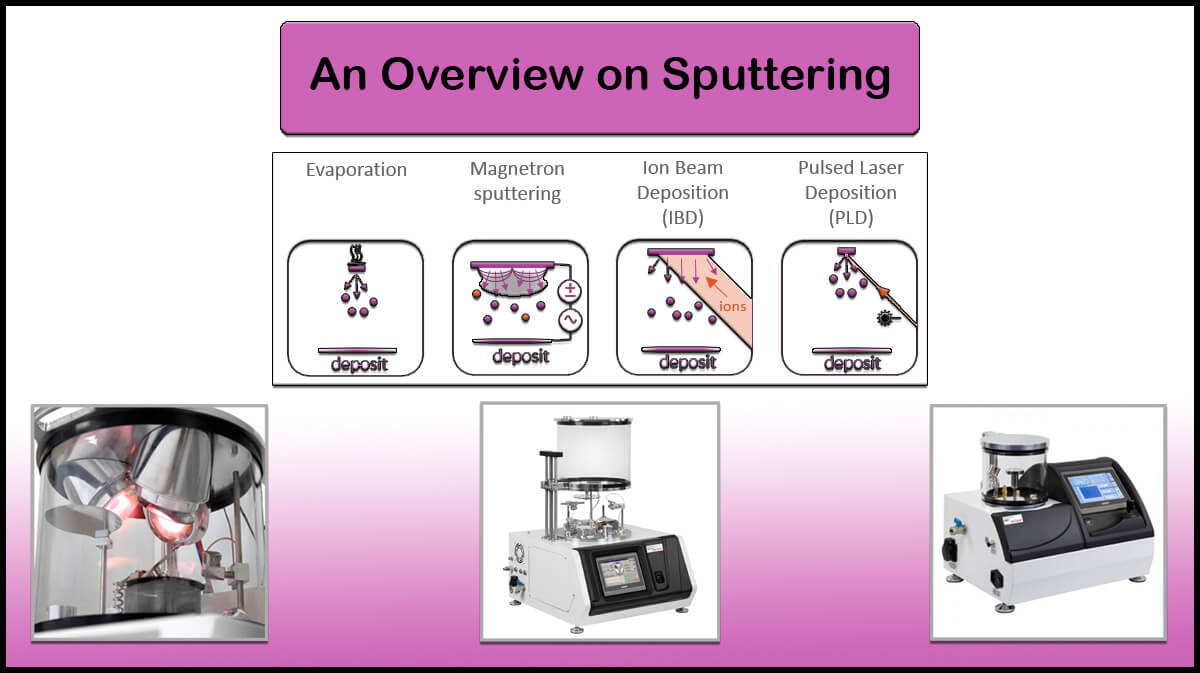
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a set of vacuum deposition methods in which a solid material vaporizes in a vacuum environment and is deposit on the substrate as a thin film. The most common methods of PVD are Sputtering and Thermal Evaporation. Because in the PVD process, the material is transported and accumulated atom-by-atom or molecule by molecule in a vacuum to the substrate surface, the deposited films have high purity and efficiency that for many applications compared to other deposition methods are preferred.
For example, in the construction of the most important part of any microchip and semiconductor device, durable protective layers, optical lenses, solar panels and many parts and medical devices, the PVD thin film provides basic functional characteristics for the final product. In general, wherever there is a need for coating with very thin, pure, durable and clean thin films, PVD is the key to solving the problem.
Hardness of Thin Films Deposited by PVD Method
Atom-to-atom deposition in PVD allows control of density, stoichiometry and atomic structure of the thin film. By using the appropriate materials and creating special conditions during the coating process, coatings with desirable properties such as hardness, lubricity and good adhesion can be created on various surfaces. For example, some hard coatings can reduce friction and protect their underside from damage.
The field of application of these friction-reducing coatings is very wide. The aerospace and defense industries, automobiles, cutting tools, rollers and many other cases in which friction reduction is very important, are all applications of coatings created by the PVD method. Titanium nitride coatings and the like are also among the coatings that, in addition to being beautiful, have a high resistance to abrasion and corrosion and are used to cover building valves and door handles that are in constant contact with the hand.
PVD is Environment Friendly
The PVD method involves environmentally friendly processes and, in comparison with other coating methods such as chemical plating, drastically reduces the use of toxic raw materials, chemical reactions, and disposal of chemicals.
Advantages of PVD
Its advantages include the following:
- PVD-coated thin films are more resistant to corrosion than coatings made using other coating processes such as plating. Most PVD coatings are impact resistant and also very abrasion resistant. These coatings are often able to withstand high temperatures
- High purity of the deposited thin films and the possibility of controlling the structure of the layers
- Thin films are cheaper bulk of material (for example, a thin layer of gold is much cheaper than a piece of gold)
- Using the PVD method, it is possible to deposit almost any type of inorganic material and some organic materials on a diverse and wide group of surfaces and substrates
- High environmental compatibility
- Provide a variety of techniques for deposition of a specific material
Disadvantages of PVD
- Limitations on the coverage of parts with complex geometric shapes. Of course, this limitation has been largely overcome by various methods of moving the substrate
- Some PVD methods and techniques require high attention and accuracy of the user due to the high vacuum and high temperature of the coating environment.
- Cooling water circulation systems are needed to dissipate the generated heat load and prevent damage to the components of the coating systems
Vacuum deposition systems manufactured by Vac Coat Ltd., using Physical Vapor Deposition coating techniques, have made it possible for users to deposit a wide range of materials on different substrates, depending on their desired performance. The possibility of using two PVD techniques in one vacuum deposition system has eliminated the problems of buying different machines for deposition of different materials. Versatile deposition system to do sputtering and thermal evaporation deposition DST3-T model and coating system versatile to do sputtering and carbon coating from carbon thread and rod in DSCR and DSCT models, including multifunctional models of Vac Coat Ltd. products.






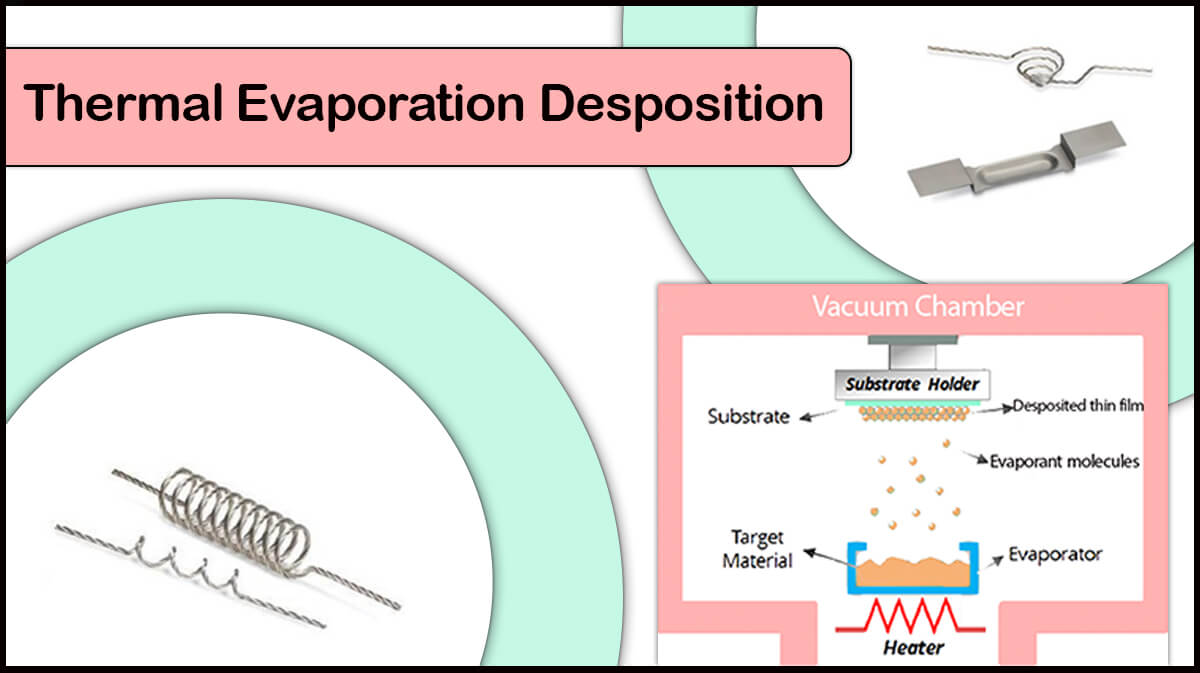



How to deposit cobalt thin film and maintain its magnetic properties?
Cobalt can easily alloy with tungsten boats during thermal evaporation, so the deposited layer may not preserve cobalt magnetic properties. Using an alumina coated tungsten boat to prevent alloying process can solve the problem. However, the boat’s lifetime is short (less than 3 runs) and should be treated gently since it gets brittle after the deposition.
Why choose PVD coatings?
PVD coatings offer high purity, excellent adhesion, durability, corrosion and wear resistance. They’re environmentally friendly and cost-effective due to minimal material usage.